The Evolution of Heart Monitoring
Electrocardiography (ECG) has revolutionized the way we understand and diagnose heart conditions. From its inception in the early 20th century to its current role in modern medicine, ECG technology has undergone significant advancements. This article explores the history of ECG, highlighting key milestones and innovations that have shaped its development.
1. The Beginnings: Early Electrical Experiments
- Galvani and Volta (18th Century): The story of ECG begins with the work of Luigi Galvani and Alessandro Volta. Galvani’s experiments with frog legs demonstrated that electrical impulses could trigger muscle contractions. Volta’s work furthered the understanding of electricity, laying the groundwork for future research in bioelectrical phenomena.
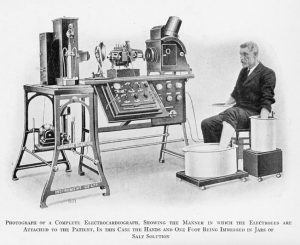
- Waller’s Discovery (1887): The first significant step toward ECG as we know it was taken by Augustus D. Waller. Using a capillary electrometer, Waller recorded the electrical activity of the human heart for the first time. This groundbreaking work showed that we can detect and measure the electrical impulses generated by the heart.
2. The Birth of Modern Electrocardiography
- Einthoven’s Innovations (1903): The Dutch physiologist Willem Einthoven is credited with the development of the modern ECG. He invented the string galvanometer, an instrument that could measure the heart’s electrical activity with high precision. Einthoven’s work allowed for the creation of the first standard ECG waveform, which he termed the “Einthoven triangle” to represent the heart’s electrical activity in three dimensions. The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded to Einthoven in 1924 for his contributions.
- Standardization and Advances (1920s-1930s): Following Einthoven’s innovations, the ECG underwent several advancements. The introduction of the first commercial ECG machines made the technology more accessible to physicians. This period also saw the standardization of the 12-lead ECG system, which provided a comprehensive view of the heart’s electrical activity from different angles.

3. The Rise of Digital Technology
- Digital ECGs (1960s-1980s): The development of digital technology revolutionized ECG recording and analysis. Early digital ECG machines replaced cumbersome analog systems, offering improved accuracy, ease of use, and the ability to store and analyze data electronically.
- Computerized Analysis (1990s-2000s): The advent of computerized ECG systems further enhanced diagnostic capabilities. Researchers developed software algorithms to analyze ECG data, identify arrhythmias, and assist in diagnosing various heart conditions. These advancements enabled more efficient and accurate interpretation of ECGs.

4. Modern Innovations and Future Directions
- Portable and Wearable ECG Devices (2000s-Present): Recent advancements have led to the development of portable and wearable ECG devices. These technologies allow for continuous heart monitoring and real-time data transmission, offering patients and healthcare providers greater flexibility in managing heart health.
- Integration with Mobile Health (mHealth): The integration of ECG technology with mobile health applications has enabled patients to monitor their heart health using smartphones and other devices. This innovation supports remote monitoring and personalized healthcare.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning technologies are increasingly being used to enhance ECG analysis. These tools can improve the accuracy of arrhythmia detection, predict heart disease risk, and provide insights into patient health trends.
A Journey Through Time
The history of ECG is a testament to the remarkable progress in medical science and technology. From early experiments with electrical impulses to sophisticated digital and wearable devices, ECG has become an essential tool in diagnosing and managing heart conditions. As technology continues to advance, ECG will undoubtedly evolve further, offering even greater insights into cardiovascular health.